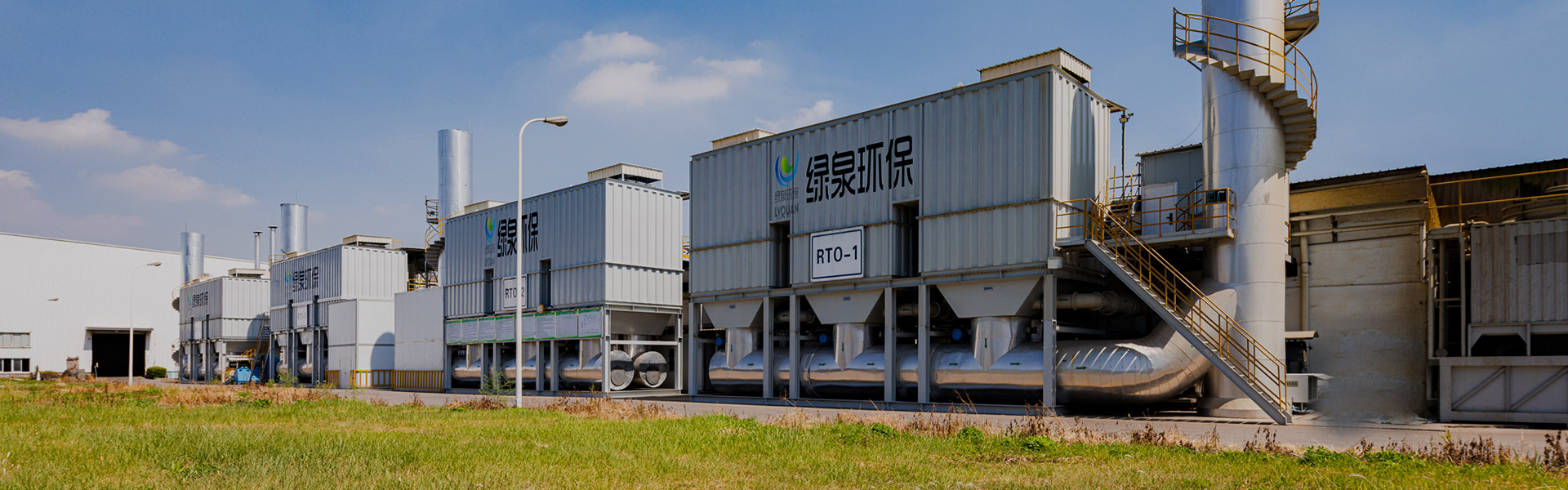
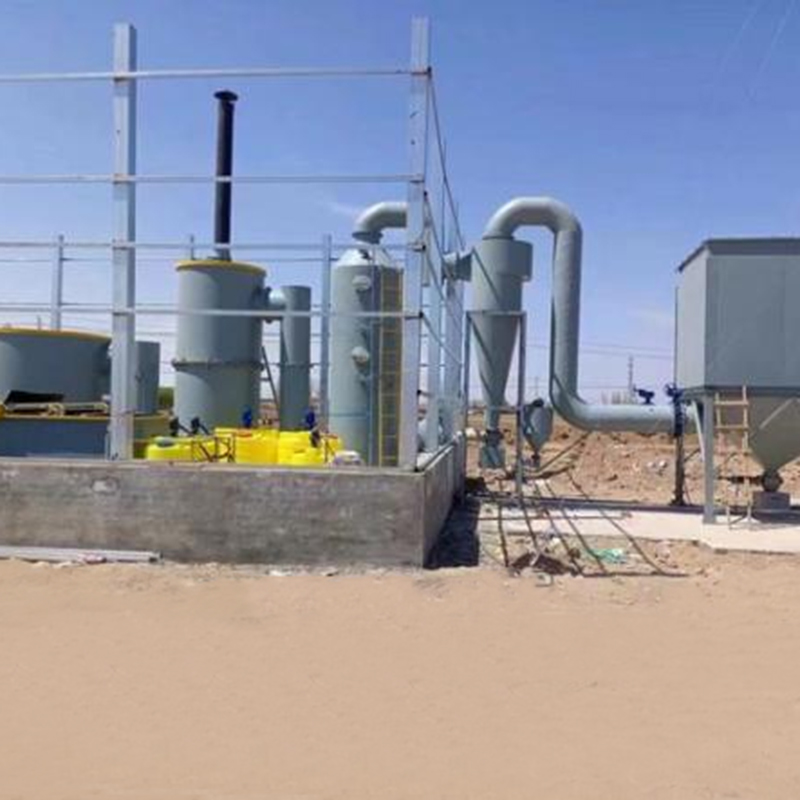
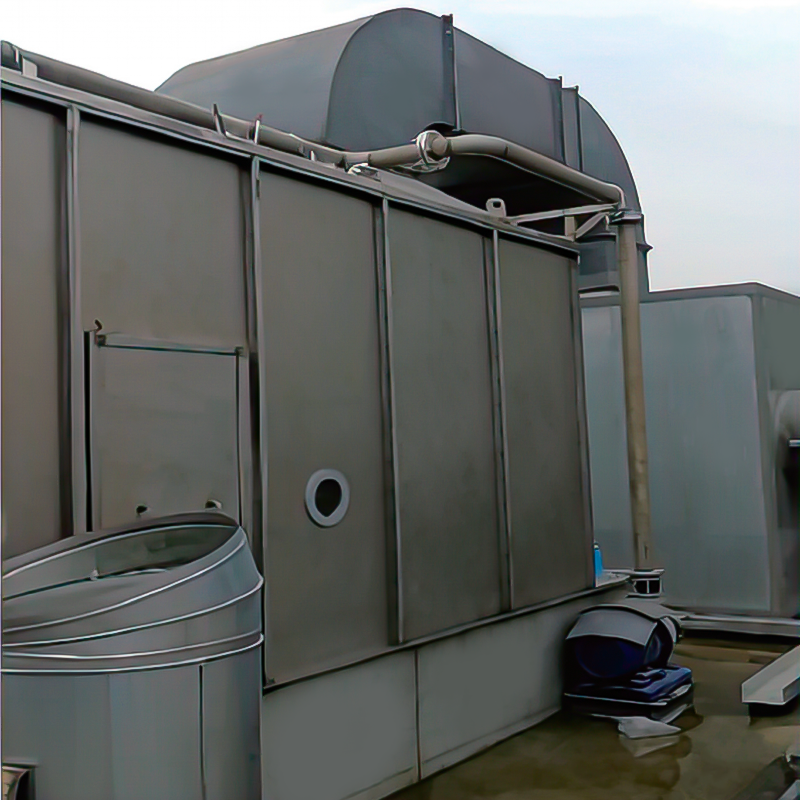
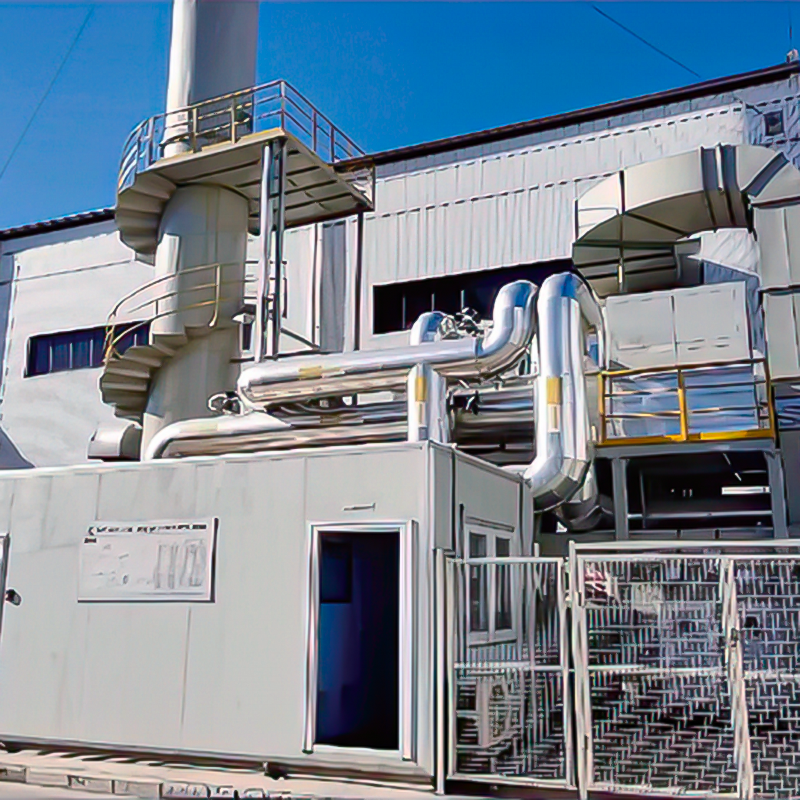
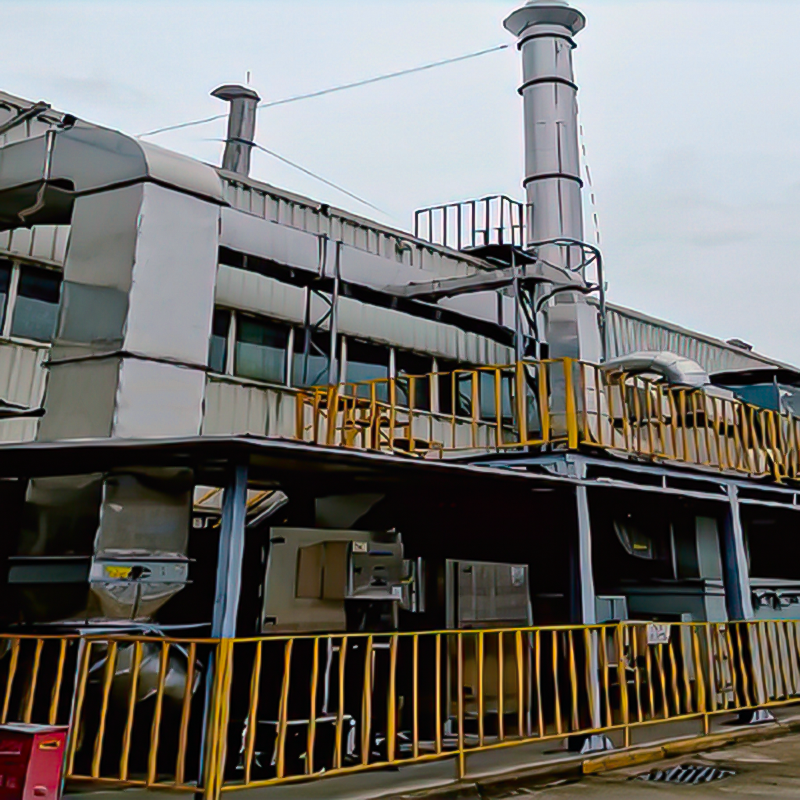
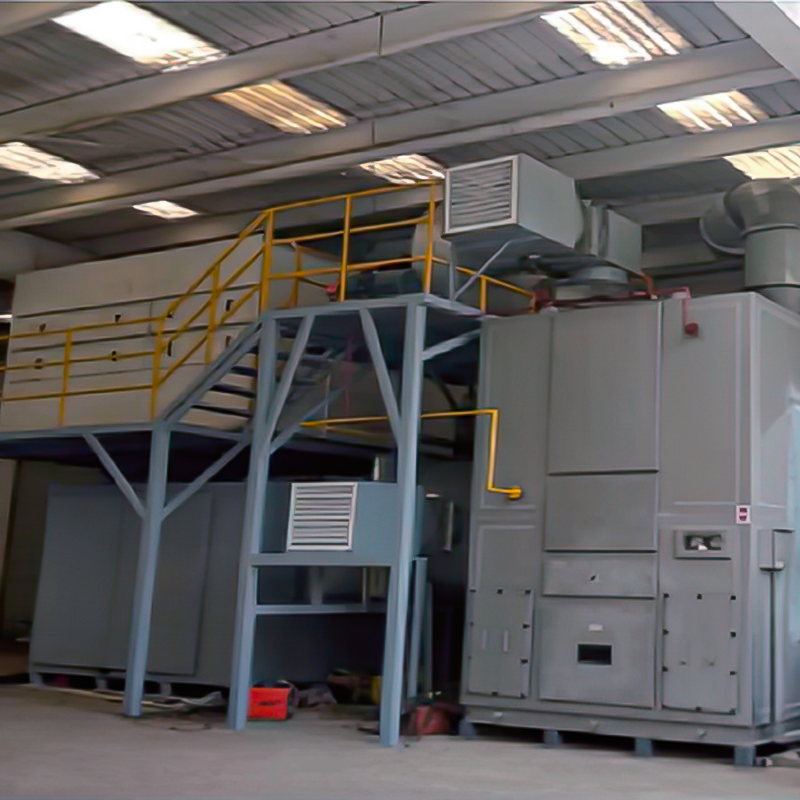
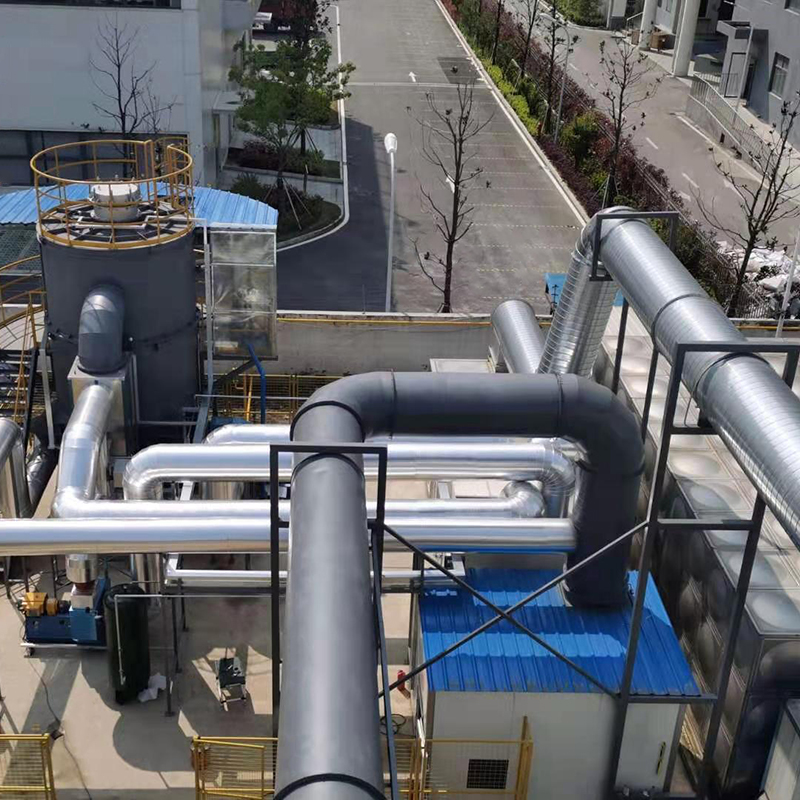
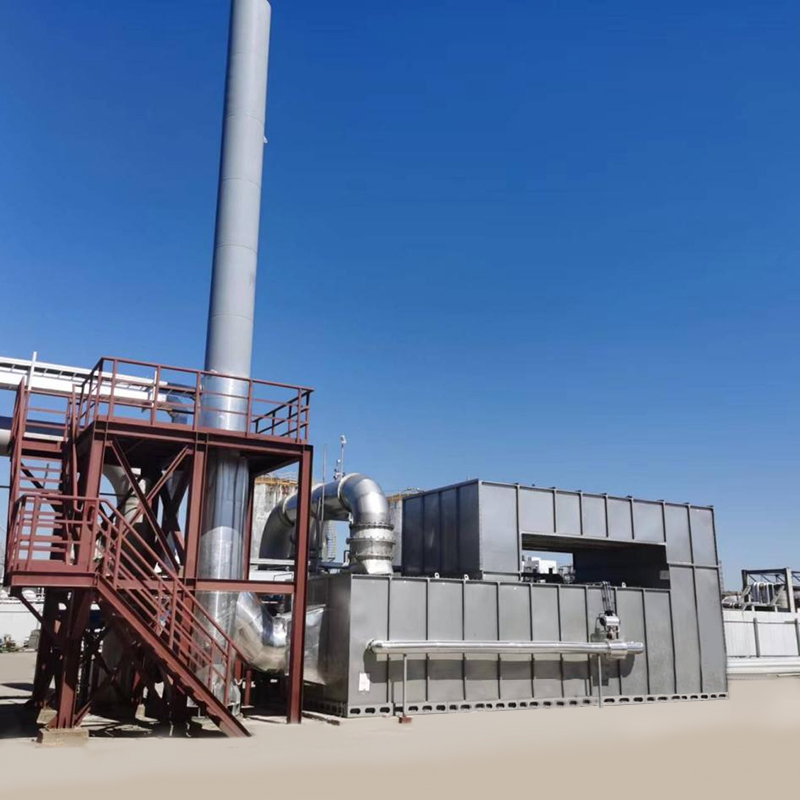
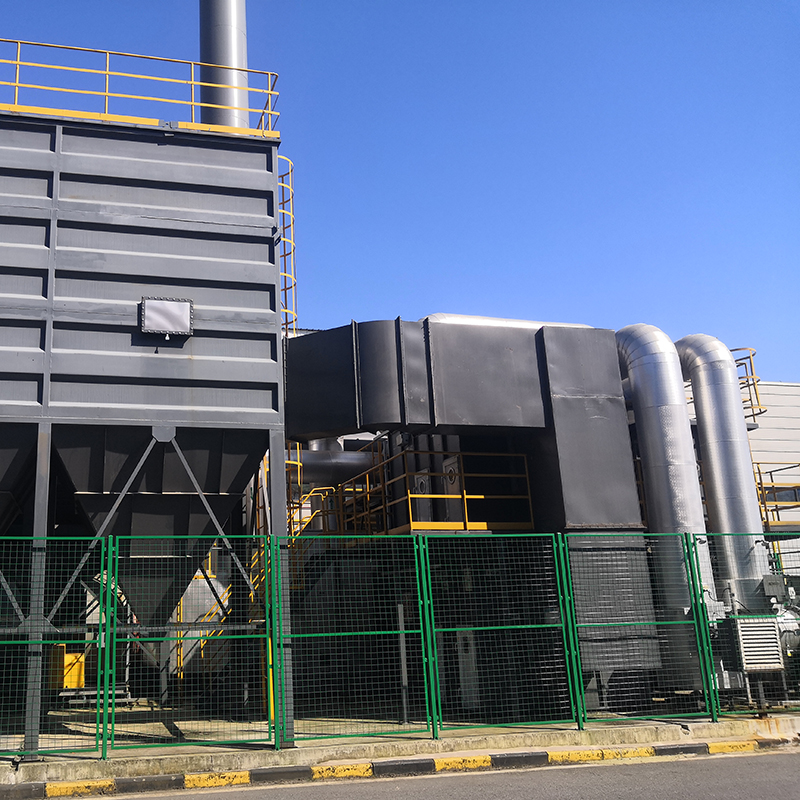
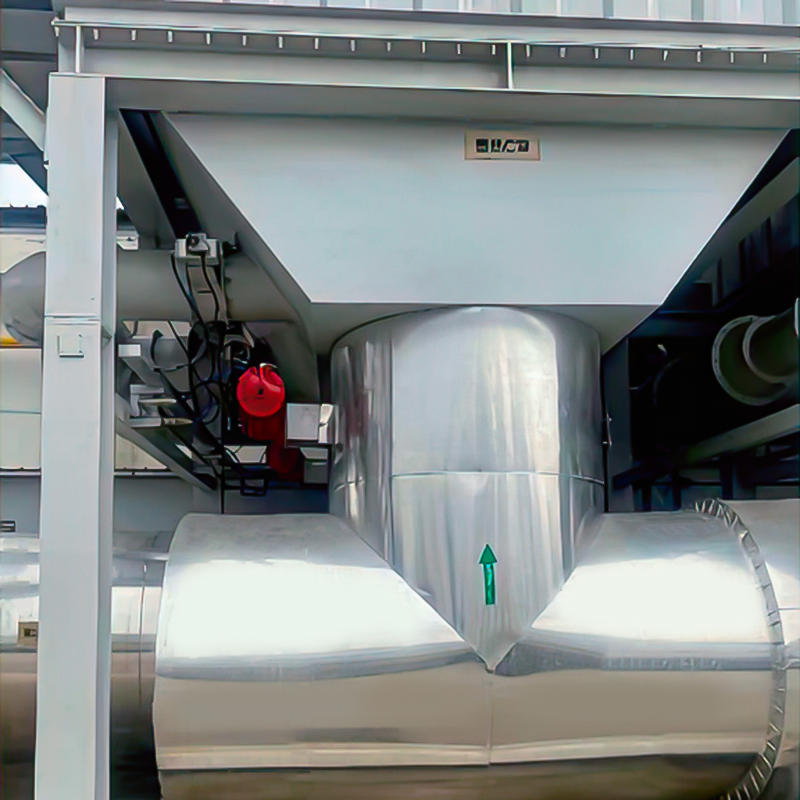
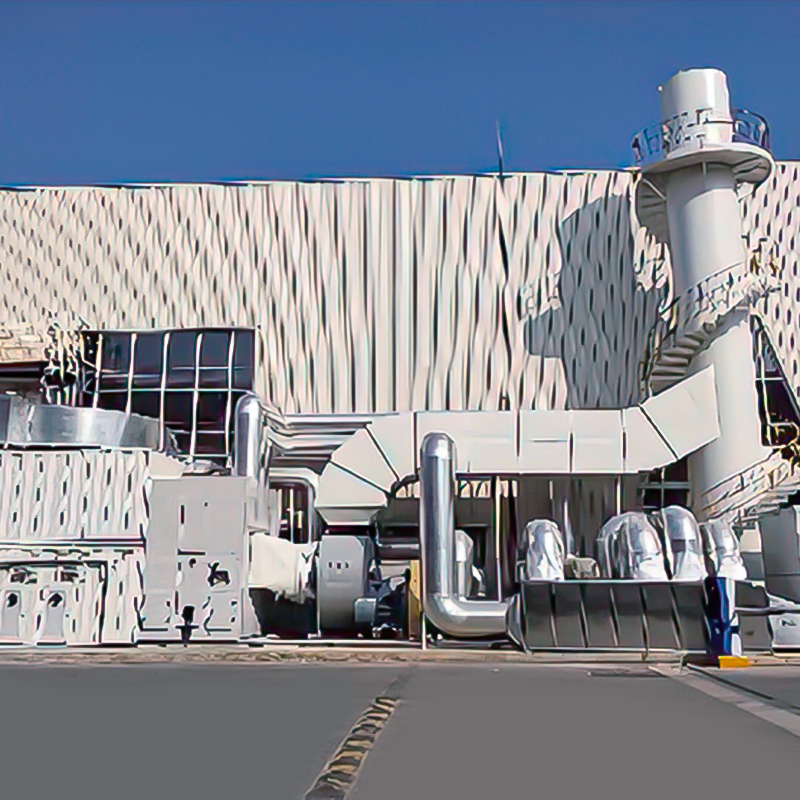
2D Drawing
+催化氧化焚烧设备co.jpg)
+催化氧化焚烧设备co-1.jpg)
Operating Principle
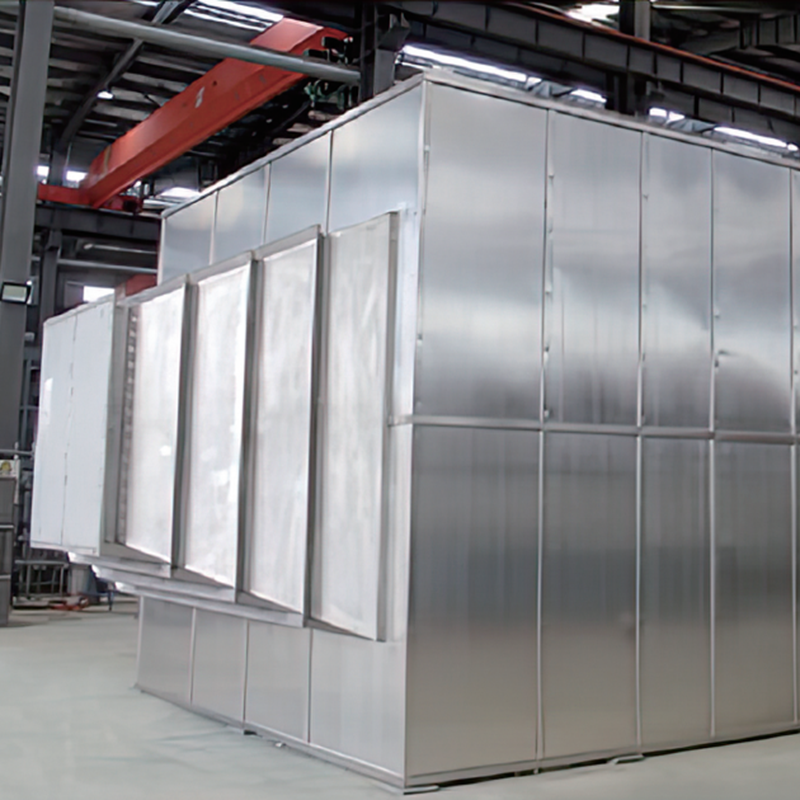
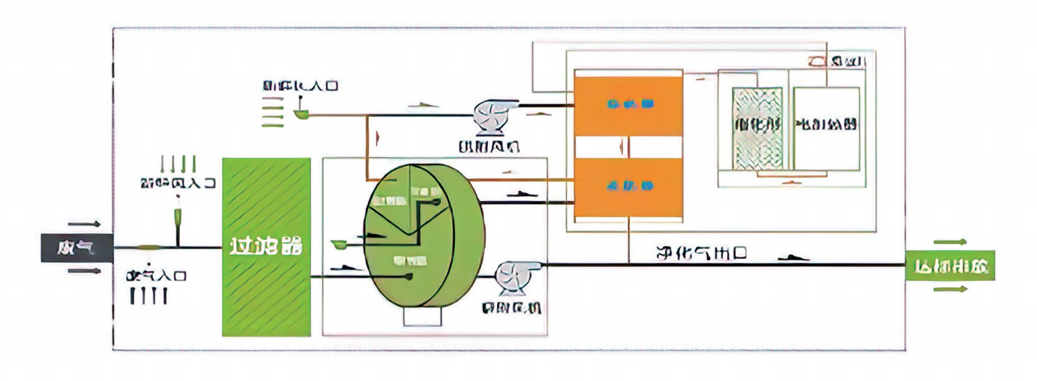
1. Adsorption stage: Organic waste gas passes through the zeolite rotary wheel for adsorption and can be directly discharged after meeting the standard. The size of the zeolite molecular sieve aperture can selectively adsorb different sizes of waste gas molecules.
2. Desorption stage: The zeolite rotary wheel always maintains a very slow rotation. After the adsorption in the processing area is saturated, the organic waste gas adsorbed in the zeolite is desorbed by blowing with hot air through the regeneration area.
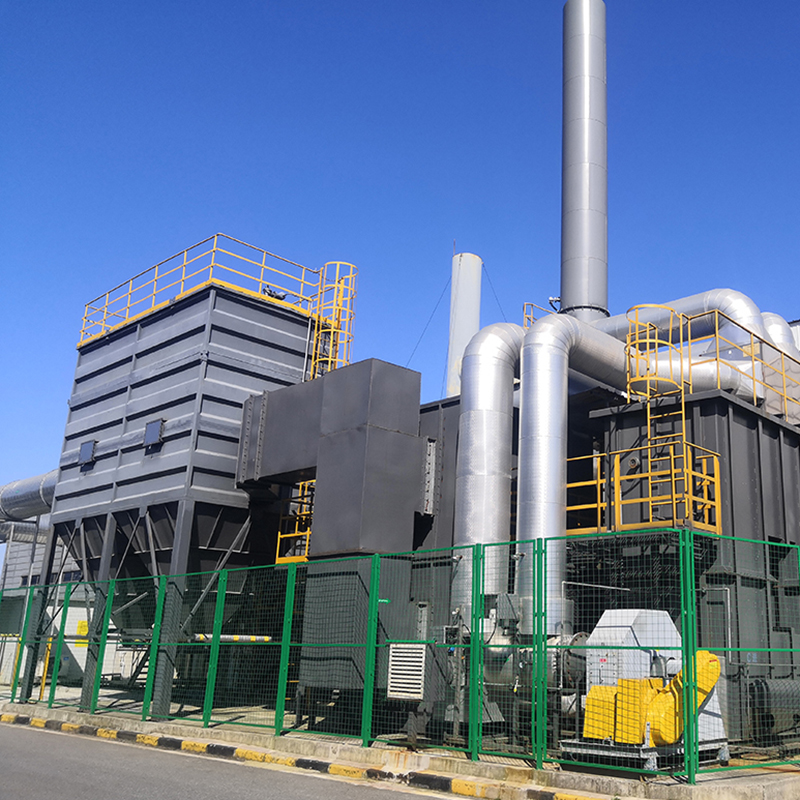
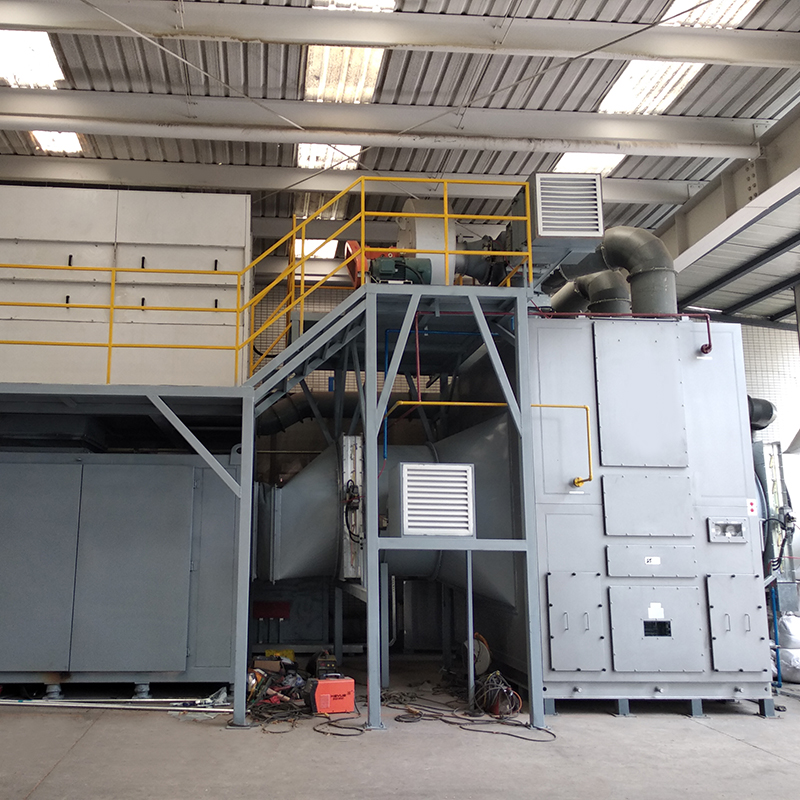
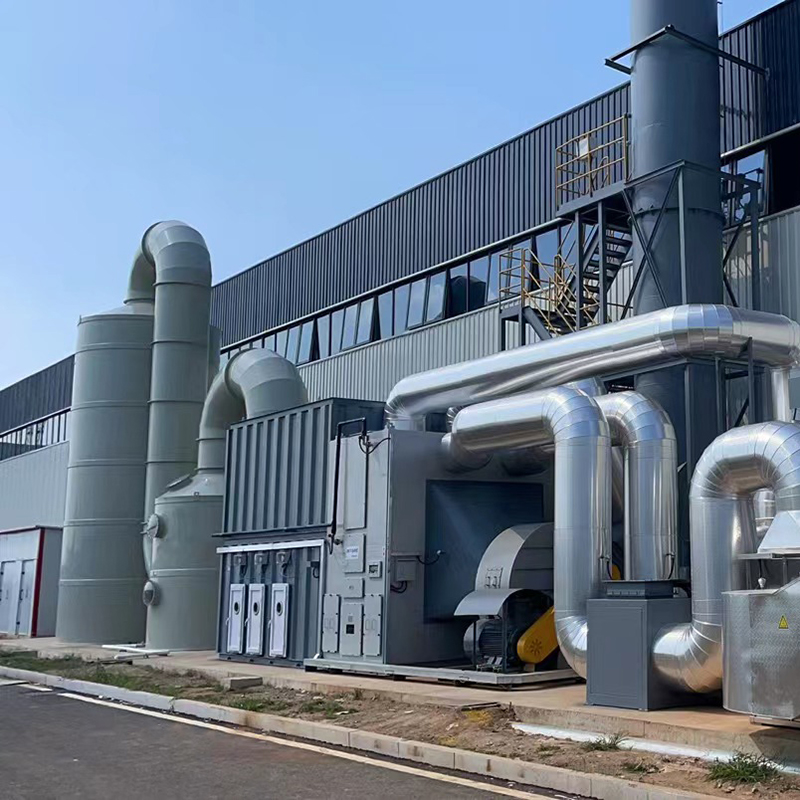
3. Catalytic combustion stage: The zeolite rotary wheel concentration device captures and collects waste gas molecules from the low concentration and high air volume waste gas, and adsorbs them on the zeolite. The high concentration and low air volume waste gas desorbed can directly enter the catalytic combustion equipment for low-temperature catalytic combustion at a combustion temperature of 300~450°C.
4. Zeolite rotary wheel recovery stage: After the zeolite rotary wheel is regenerated by high-temperature heating, the adsorption effect will deteriorate with the increase of the zeolite temperature. To maintain the zeolite's ability to repeatedly adsorb waste gases, it is essential to cool the zeolite using a cooling fan. This process ensures the zeolite retains its cyclic adsorption capabilities.
Characteristics Of Voc Concentration Equipment
High purification efficiency: The theoretical removal rate of the wheel adsorption can reach up to 98.5% (except for specific chemicals).
High desorption efficiency: Organic compounds with boiling points below 220°C can basically be detached.
Small floor space: Compared with other adsorption equipment, it has a relatively small size.
Low fire risk: Compared with activated carbon adsorption, zeolite wheels are non-combustible and have no risk of ignition during the desorption process.
Fast adsorption and desorption: Short adsorption time, easy saturation, high desorption efficiency, and short cycles.

Conditions For Selection Of Catalytic Combustion
1. The waste gas must not contain components that will poison or permanently deactivate the catalyst, such as chlorine, sulfur, halogen, heavy metals, etc.
2. The mixed waste gas entering the catalytic combustion equipment must have a concentration lower than 1/4 LEL (lower explosive limit) range.
3. The maximum temperature used in catalytic combustion is less than 600℃. High-heat substances and hizh-concentration gases need to be diluted to prevent the temperature of the reaction chamber from exceeding the limit and causing catalyst deactivation, thereby preventing the catalytic reduction reaction from being carried out.
4. The gas entering the catalytic combustion must not contain dust particles or oil mist that can cause blockage or cause a fire.


 English
English русский
русский Français
Français Español
Español عربى
عربى