LQ-RRTO Rotary heat-storage high-temperature incineration equipment
Cat:Equipment
Overview Of Tower-Type RTO Our company offers two types of rotary RTO, which are the rotary RTO and the single barrel multi-valve RTO. The rotary RTO,...
See DetailsSolid waste incineration furnaces are crucial equipment for treating solid waste (such as municipal solid waste and industrial waste). They convert waste into harmless gases, residues, and heat energy through high-temperature combustion, achieving the harmlessness, volume reduction, and resource recovery of waste. However, during long-term use, solid waste incineration furnaces may experience some common faults, which not only affect the furnace's operating efficiency but may also lead to environmental pollution and safety hazards. Therefore, timely detection and resolution of these problems are essential to ensuring stable equipment operation and reducing environmental impact.
Common Faults and Their Causes
1. Abnormal Fluctuations in Furnace Temperature
Symptoms: Significant fluctuations in furnace temperature may lead to incomplete combustion or insufficient combustion. Too low a temperature makes complete combustion difficult; too high a temperature may result in fuel waste, furnace damage, and increased pollutant emissions.
Possible Causes:
Uneven Combustion Air Supply: Insufficient or uneven air supply leads to incomplete combustion and temperature fluctuations.
Uneven Waste Distribution in the Furnace: Uneven waste accumulation causes localized areas of excessively low or high temperatures.
Burner Malfunction: Unstable burner operation results in uneven flames and ineffective waste heating.
Solutions:
Check the Air Supply System: Ensure the air supply system is functioning properly, and that components such as fans and dampers are not malfunctioning or blocked.
Adjust Waste Feed Rate and Method: Properly control the amount and distribution of waste to ensure even distribution within the furnace.
Regularly Inspect the Burner: Regularly clean the burner and nozzles to ensure even flame distribution. Replace any damaged burners promptly.
2. Excessive Flue Gas Emissions
Symptoms: Emissions of harmful gases (such as dioxins, nitrogen oxides, and carbon dioxide) in the flue gas exceed standards, potentially polluting the surrounding environment and air quality in severe cases.
Possible Causes:
Insufficient Incineration Temperature: Low temperatures lead to incomplete combustion of waste, producing large amounts of harmful gases.
Faulty Waste Gas Treatment System: Malfunctions in the flue gas desulfurization, denitrification, or dust removal devices may prevent effective treatment of harmful gases.
Incomplete Combustion: Insufficient oxygen supply in the incinerator or low calorific value of the waste can easily lead to incomplete combustion, resulting in excessive amounts of harmful substances.
Solutions:
Increase Incineration Temperature: Ensure the furnace temperature reaches the optimal combustion temperature for waste, typically above 800°C, to ensure complete combustion.
Inspect the Waste Gas Treatment System: Regularly inspect all facilities in the flue gas treatment system, such as the desulfurization tower, denitrification device, and dust collector, to ensure their proper operation.
Optimize Waste Input and Mixing: By rationally controlling the type, amount, and mixing method of waste, ensure complete combustion of waste in the furnace and reduce the generation of harmful gases.
3. Furnace Ash Accumulation or Blockage
Symptoms: Excessive ash accumulation or blockage in the furnace leads to decreased combustion efficiency and may even cause equipment malfunction or shutdown.
Possible Causes:
Excessive Non-combustible Materials in Waste: Some wastes may contain high levels of minerals or metals that cannot be completely burned and easily accumulate in the furnace.
Improper Furnace Temperature Control: Insufficient temperature results in incomplete combustion of waste, leading to ash accumulation in the furnace.
Inadequate Furnace Cleaning: Prolonged lack of cleaning leads to ash buildup in the furnace, hindering normal waste combustion.
Solutions:
Regular Furnace Cleaning: Regularly clean the furnace to remove accumulated ash and ensure unobstructed flow.
Control Waste Input: Prevent excessive waste containing non-combustible materials from entering the furnace to reduce ash accumulation.
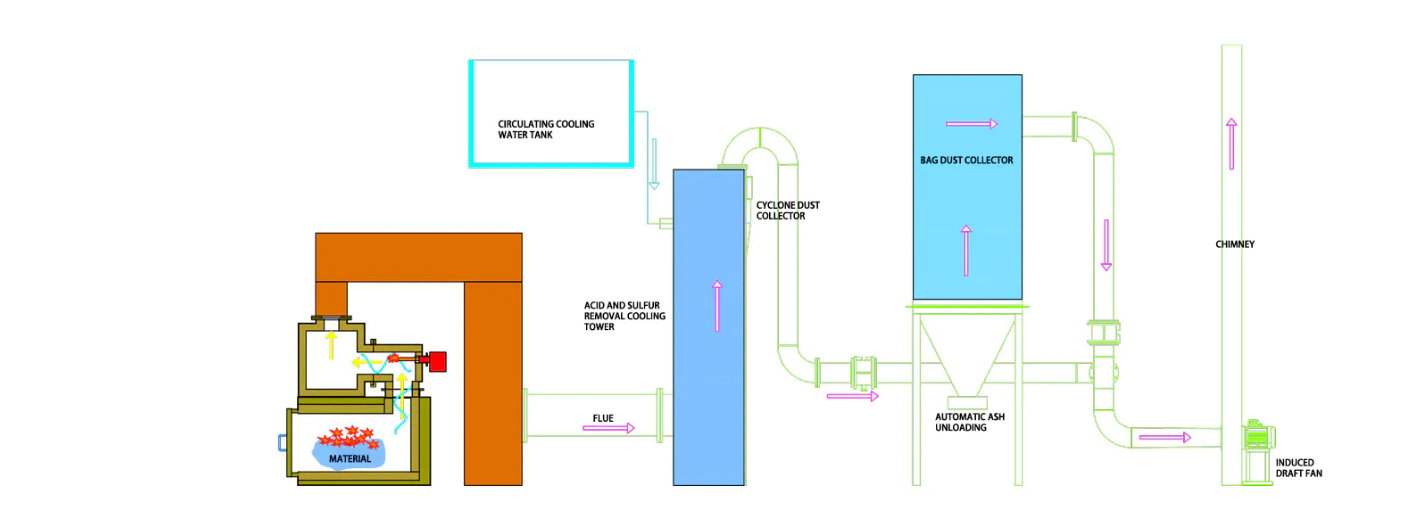
4. Furnace Body Leakage or External Gas Leakage
Symptoms: Leaks occur in the furnace body or flue gas ducts, leading to poor furnace airtightness, allowing exhaust gas to leak out or air to enter the furnace, affecting combustion efficiency.
Possible Causes:
Aging or Damaged Sealing Rings: Aging or damage to the furnace body's sealing parts leads to gas leakage.
Poor Welding of Pipelines or Furnace Body: Poorly done welding results in cracks in the furnace body or pipelines, causing gas leakage.
Improper Operation: Improper operation or excessively high furnace pressure may damage the furnace body or cause leakage.
Solutions:
Regularly Inspect Sealing Components: Regularly inspect the sealing rings and welded parts of the furnace body and pipelines, and replace any aged or damaged parts promptly.
Repair Cracks and Damaged Areas: Repair cracks in the furnace body and pipelines to prevent gas leakage.
Maintain Appropriate Furnace Pressure: Avoid excessively high furnace pressure caused by improper operation to maintain stable furnace operation.
5. Excessive Slag or Poor Discharge
Symptoms: Excessive slag or poor discharge leads to excessive slag accumulation during incineration, hindering timely discharge and affecting normal equipment operation.
Possible Causes:
Complex Waste Composition: The waste contains a large amount of non-combustible components such as metals and glass, resulting in increased residue.
Slag Discharge System Malfunction: A malfunction in the slag discharge system prevents timely slag removal.
Solutions:
Optimize Waste Classification: Minimize the entry of non-combustible materials to avoid excessive slag production.
Inspect the Slag Discharge System: Regularly inspect the slag discharge system to ensure smooth operation and timely slag removal.
Solid waste incinerators, as crucial equipment for waste treatment, may experience various malfunctions during operation. However, timely detection and appropriate solutions can effectively prevent these problems from worsening. By strengthening daily equipment inspection and maintenance, optimizing the incineration process, and ensuring the effective operation of the exhaust gas treatment system, we can improve incinerator efficiency, reduce environmental pollution, and ensure safe and harmless waste treatment.
